ECONOMIC GROWTH
Causes of Economics Growth:
Long Term growth is from an increase in quality or quantity of factors of production:
-
Land
-
Labour
-
Capital
-
Enterprise
Economic stability and sound macroeconomic policies:
Stability: Particularly growth of AD backed up by sensible government policies means that business uncertainties can be reduced and lead towards a more stable economy.
Increasing labour activity participation: Countries with high growing populations mean that there is a likely chance of a fall in living standards.
Why? Because there are more children/people in the country that are consuming without producing. This could be a result of aging population as well as more children being born.
This would lead to an increase in GDP however there will not be an increase the GDP per Capita.
True economic growth is when the percentage of population that is actively employed, is high.
Factors that have and can lead to higher employment:
-
More relaxed social attitudes towards women working
-
Flexible working time. Eg: Part-Time/Full-Time options.
-
Tougher benefits system: Lower benefits will give people an incentive to find work.
-
Incentives via the tax system: Eg: Working Tax Credit
-
Re-training schemes to overcome occupational immobility: Eg: Mine worker retrain with IT skills. People with expired technological skills are retrained.
Occupational Immobility: When workers find it difficult to change jobs because they don’t have the required skills that are need for the given job. Eg: A miner would have inadequate skills to work in the IT/Marketing sector.
Increasing labour productivity:
Labour productivity is the key for long-term economic growth. Labour productivity is measured via output per worker, per hour.
The key factors of high productivity are improvements in Human and Physical Capital.
Investment in Physical Capital:
Use physical capital to be more productively efficient.
Keeping up with new technologies and investing with them will mean that firms can be more diverse and keep up with consumer needs. This allows them to also be more dynamically efficient and be competitive in the long run. However it’s essential that staff are trained to use this capitally efficiently which may cost the government more money.
There would be long – run advantages training these workers. However, there could also be disadvantages as money may be wasted. Technology is developing at an extremely high rate today which may be constantly spending to train workers over and over.
The government can encourage the use of more physical capital through these supply-side policies:
-
Lower taxation on business profits & wealth
-
Tax Relief: For high spending on research and development
-
Promoting links between universities and businesses
-
Reforming trade union legislation (laws) do business are easier to manage
-
Privatisation: This will mean opening up business to the stock exchange discipline & sources of finance
-
Tougher competition policies: This will help so firms do not feel demotivated by other firms.
-
Encourage foreign investment into the UK, bringing ‘best practice’ from main international competitors. This will help to increase quality.
-
Encourage macroeconomics stability
Improved human capital- education and training:
Invest in education and training. An educated workforce will be more productive and will generate more economics growth.
CHAIN OF ANALYSIS: More in work = More people earning = GDP per Capita increase = More money to spend = AD increases = Can lead to more jobs as more goods demanded, especially if they are domestic. [MULTIPLIER]
However: You caan evaluate by saying that there will be growing inflationary pressures as the economy enter positive output gap. Also, Educating and Training a workforce means advantages in the long run. It takes years and years of educating and training to improve conditions.
Enterprise:
Encouraging a motivation and enterprise culture is extremely important so people can have a more entrepreneurial streak and contribute to economic growth in the long run.
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF ECONOMIC GROWTH:
ADVANTAGES:
-
Rise of living standards in households due to the increase in GDP per Capita
-
Helps to reduce if not eliminate Absolute Poverty
-
Rise in tax revenue for government without having to raise tax rates = Rise in National Income
Can be used to help finance schemes, such as; Helping the poor
Can be used to provide important public and merit goods.
Can even help to correct negative externalities.
DISADVANTAGES:
-
There will be unavoidable opportunity costs. EG: Growth may be at expense of environment
This can happen if there is a rapid development in the industrial sector without pollution controls = Negative externalities.
This is a fear for Chinese and Indian economies.
-
May result in a depletion of non-renewable resources, such as; Oil.
-
May widen the gap between the rich and poor
Could increase the level of Relative Poverty.
-
A lot of goods and services may not result in satisfaction but in people just wanting more and more goods and services. This is an issue as resources are finite.
FOR EXAMPLE: A few years ago, household were more than happy with one car. Now however, most have 2 cars and maybe even more.
DIAGRAM TIP: Add in a Boom/Bust diagram to illustrate economic growth. It will definetly get you marks and is very simple to draw. It's like the biggest trick in the book. Draw it in for the sake of it, and you'll get marks!
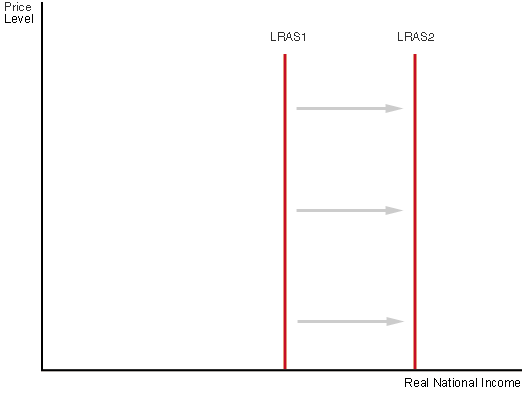
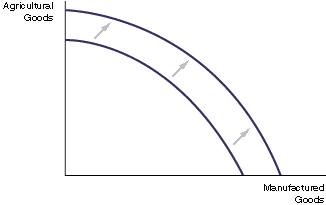
An increase in productive capacity via the improvement of quantity/quality in a factor of production can be shown via one of the two graphs below.