TYPES/CAUSES OF INFLATION
Stagflation:
When high level of unemployment occur at the same time as high levels of inflation.
Explained further on the 'Expectations-Augmened Phillips Curve (EAPC)'
Cost-Push Inflation:
This is when costs of production push up the price level. Prices are raised simply to maintain the profit margin. Cost-Push Inflation may be caused by several factors.
On a diagram: SRAS WILL SHIFT LEFT
-
A rise in the costs of imported materials: For example: If there has been inflation in Spain, it means that things are more expensive to import. This would mean that if we use Spain as a source to supply resources, producing our products will automatically rise in costs. This makes it expensive for us to produce which means that we will have to raise prices in order maintain our profits.
-
Rising labour costs: If wages rise and firms have to pay their workers more money as a salary they will have to make up the money lost somewhere else. This will be done through raising prices which will lead to higher prices for consumers, and as a result Cost-Push Inflation will occur.
-
Higher Indirect Taxes: If taxes are imposed on firms, a portion of them will usually be passed onto consumers. In particular goods that have an inelastic PED.
-
Wage-Price Spirals: This is when workers ‘think’ that inflation will rise. When this happens they negotiate higher wages in order to cover the future rise in prices. When this happens there is a risk that a ’wage-price spiral’ will occur where firms will increase their prices so that they can maintain their profits.
Demand-Pull Inflation:
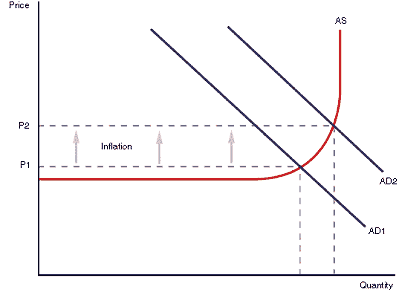
This is when there is a small amount of spare capacity in the economy. So for example… If Labour is being gully utilized it means that there is little spare capacity due to the high employment. This will mean more people are with jobs and earning a salary. Automatically, Aggregate Demand will increase as they will be spending more. Due to the high demand, price levels will automatically rise. This will lead to Demand-Pull Inflation.
On a diagram: AD WILL SHIFT TO THE RIGHT
EXAM TIP: When talking about demand pull inflation, if you are evaluating or talking about Investment, remember that it may increase AD in the short run but it will increase AS in the long run, hence increasing the LRAS.

DEMAND-PULL INFLATION
COST-PUSH INFLATION